Last Updated on April 15, 2024 by Ryan
- Repairing a sinkhole in your yard
- What causes a sinkhole?
- The Warning Signs of Sinkholes
- Will a sinkhole go away on its own?
- Is it possible for a sinkhole to spread?
- What are the Best Sinkhole Repair Methods?
- Size of the sinkhole
- How to Repair Smal Size Sinkholes Step By Step
- What is the Average Cost of Sinkhole Repair?
There are a few sinkhole repair methods for major sinkholes in Florida, Here we try to cover a simple solution to repair a sinkhole with small size in your backyard.
Repairing a sinkhole in your yard
The first step in sinkhole repair is to figure out what’s causing the hole to form. The source of the sinkhole problem will be revealed by excavating the affected region. Sinkholes are commonly created by the following factors:
- A pipe breaks
- Disintegrated debris
- A forgotten portion of a septic system
- A collapsing underground structure
Most people see a sinkhole as a crumbling road with vehicles and houses descending into a massive pit. Sinkholes are an eyesore on your lawn, and sinkhole repair is a must to do, we realize that. These flaws can jeopardize your family’s safety, depending on their severity. Giant sinkholes are hazardous and might endanger the structural stability of your property. These holes can have far more dangerous reasons. Sinkholes are caused by failing infrastructure under your yard’s surface or a major continuing plumbing issue.
Living with a sinkhole, regardless of its origin, may be difficult. If your lawn is currently showing signs of a sinkhole, it can be repaired.
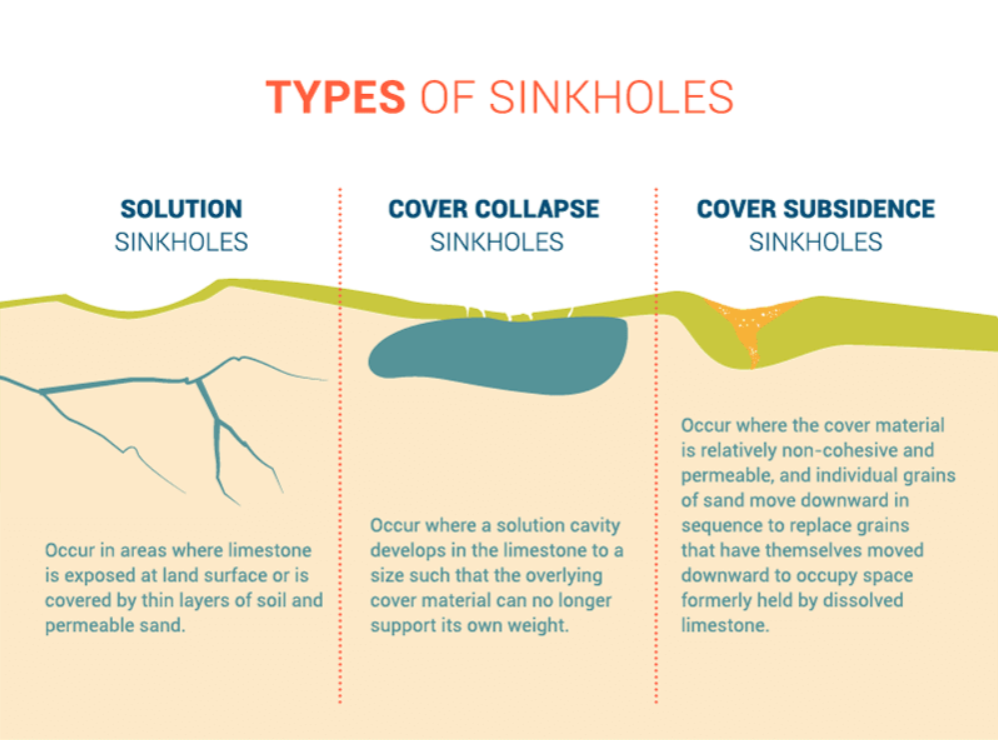
What causes a sinkhole?
A sinkhole is a weird pit in your yard that arises out of nowhere. Finding a sinkhole on your property is not a thrilling experience. Sinkholes are a terrible hazard that may emerge abruptly and unexpectedly. They come in a variety of sizes, from tiny and innocuous to enormous and hazardous. A sinkhole usually starts as a small hole in the earth and expands into a more significant depression.
- The formation of an underground hollow mainly causes sinkhole pockets. Sinkholes are widespread where a building under the surface of the ground has collapsed. Basements from homes that have been demolished for a long time may cave in.
- Steel septic tanks that have been abandoned have a propensity to corrode through and collapse. Problems like these will leave your yard with an empty hole.
- Sinkholes in your lawn can also be caused by shifting geological features. Sinkholes can arise in areas where there are naturally existing caverns and caves.
Sinkholes can also form when a drain line collapses, splits, or fractures underground. Groundwater seeps down through the dirt and into the pipe when this happens. The earth is pulled along by the lowering water as it sucks into the line, resulting in a sinkhole.
This is more common in areas with broken sewage pipes, rain leaders, and septic systems. Sinkholes may be avoided by keeping your home’s subterranean plumbing in good working order.
The Warning Signs of Sinkholes
A jagged split in the concrete or water rushing into your basement may not be the first indicator of foundation problems. There are additional, more subtle indicators that you may dismiss as “home peculiarities”!
If your walls bulge or bend, it’s possible that the foundation is causing the problem. Another indicator is separation at the corners of doors, windows, and garage doors, as well as windows that refuse to open. Other “minor” details, such as doors that won’t close or remain shut when shut and bulges in the floor, might also be indicators that something isn’t quite right.
If you see one or more of these subtle indicators in your own house, you should get your foundation inspected by an expert, reputable professional.
Will a sinkhole go away on its own?
Sinkholes do not disappear on their own. For the sinkhole to disappear, the underlying cause must be rectified and filled in. While sinkholes can develop naturally, the majority of them are caused by a single source that can be identified and remedied.
Sinkholes can be caused by collapsed constructions such as abandoned root cellars, corroded septic tanks, abandoned basements, and inadequately filled in pools. Sinkholes can also be caused by broken sewage, water, rain leader, and septic pipelines.
Is it possible for a sinkhole to spread?
It is possible for a sinkhole to expand if it is not remedied. As previously stated, the sinkhole’s cause must be eliminated before the hole may be filled up. Allowing the sinkhole to remain undisturbed or incorrectly “repaired” might result in the hole returning or, worse, expanding. Sinkholes of this size are quite dangerous.
A sinkhole that collapses might compromise the structural integrity of your home or other property. Foundations, patios, garages, pool houses, sheds, fences, decks, driveways, and automobiles are frequently damaged by large sinkholes. Falling into a sinkhole can inflict personal injury in addition to structural damage.
What are the Best Sinkhole Repair Methods?
The optimal sinkhole restoration procedure is determined by the size and stability of the hole. Replacing dirt and fixing ground cover will be sufficient for a smaller hole with the firm ground at its lowest level.
Larger holes that the landowner can excavate to bedrock can be mended by laying varied sizes of stone, gravel, and soil on top. Professional sinkhole repair methods are required for exceptionally big holes with unstable sidewalls or low spots.
A sinkhole is a depression in the earth created by groundwater eroding underlying rock, causing the dirt above it to sink. The diameter and depth of these holes vary from around 3 feet (0.9 meters) to 300 feet (91 meters). Sinkholes may be found practically anywhere, although they are most abundant in the Southeast.
Man-made sinkholes are also prevalent, and they form when a depression in a piece of property has been filled with garbage, branch cuttings, or other debris, and the subsurface support has been compromised. Regardless of the source of the sinkhole, the procedures for repairing it are the same.
Size of the sinkhole
Begin the sinkhole restoration procedure by using a long, robust pole or stick to measure the breadth and depth of the pit. If the hole is really large, getting a professional contractor who can excavate to bedrock and fill or reinforce as needed is generally the best option. If using the pole to probe the sinkhole’s edges does not result in a hard base and sides, a specialist should be contacted.
A smaller sinkhole (About 3 feet (0.9 meters)
A 3 foot (0.9 meters) broad and deep sinkhole in a residential home with a strong base and sidewalls may typically be fixed by adding earth. A few inches of the earth should be layered in and carefully tamped down by the property owner. Rep this procedure until the tamped earth has filled the hole to the level of the surface. Ground cover should be replaced if it has been lost.
Large depression Sinkholes (About 3 feet to 6 feet wide and deep (0.9 meters to 1.8 meters)
Sinkhole fixing entails piling rock, sand, and soil in a big depression that is 3 feet to 6 feet broad and deep (0.9 meters to 1.8 meters) and that the property owner may excavate to bedrock. Begin by laying a layer of stones the size of cabbages on the bottom of the dug hole. Place a layer of smaller stones, roughly the size of billiard balls, on top of these. Fill up the gaps between the stone layers with gravel.
Over the gravel lay a synthetic construction fabric, also known as a geotextile, on top of the stacked stone. This is a tough, stretchy cloth that will keep sand and grime from washing through the stone layers. Sand should be layered on top of the building fabric, and soil should be layered on top of the sand to reach ground level.
How to Repair Smal Size Sinkholes Step By Step
Sinkholes form when subterranean soft rock, such as limestone, gypsum, or other carbonate rock, wears away over time. This type of terrain is referred to as “karst.” The supporting material above the subsurface hole eventually falls, exposing the sinkhole.
Sinkholes arise abruptly and without notice when property owners are unaware that their homes are constructed on karst ground. To fill a sinkhole, start by pouring a concrete plug into the hole’s bottom. Fill the rest of the sinkhole with clay sand, and then cover it with topsoil. There are 6-7 sinkhole repair methods for big-size sinkholes. Here is a simple sinkhole repair method step by step:

Measuring the Sinkhole
Monitor the hole to see if it grows.
Weather events, such as a big downpour, are frequently responsible for sinkhole formation. However, once a sinkhole has developed, it can continue to expand when more limestone or other carbonate materials fall away.
Please do not attempt to fill in a sinkhole as long as it continues to expand on a daily basis. You may fill in the sinkhole once it has stopped developing and has maintained the same size for a few days.
